Glioblastoma multiforme also known as glioblastoma is a fast-growing glioma that develops from star-shaped glial cells which support the health of the nerve cells within the brain. It is the most aggressive cancer that begins within the brain and is the second most common brain tumour. Glioblastomas are characterized by the presence of small areas of necrotizing tissue that are surrounded by anaplastic cells. About three per one lakh people develop the disease a year. It most often begins around the age of sixty-four years and occurs more commonly in males than females. Radiation therapy for cancer is an important way of treating the disease. Advanced medical sciences treatment has been adopted in cancer hospital Bangalore and other cancer hospitals in India.

What is the cause of glioblastoma multiforme?
Glioblastoma cells have more genetic abnormalities than the cells of other types of astrocytoma brain cancer. Researchers believe that several different genetic mutations is involved in the development of these cancers. These genetic mutations can be caused by
- Inherited DNA defects.
- High-dose exposure to ionizing radiation
- Cumulative effects of exposure to chemicals and other carcinogens
Genetic mutation can cause a cell to break away from its normal growth and death cycle; one additional cell can produce additional copies of itself that can eventually accumulate into a tumour.
Symptoms of Glioblastoma Multiforme
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the brain tumour but also may include the following:
- Persistent Headaches
- Double or blurred Vision
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Changes in mood and personality
- Changes in ability to think and learn
- Speech difficulty of gradual onset
- Localized neurological problems
Treatment
Treating glioblastoma is very difficult due to several complication factors. There is a unique barrier, termed the “blood-brain barrier” limiting the passage of molecules, from the main bloodstream into the brain. Glioblastoma is having finger-like tentacles, which extend some more length from the main tumour mass to the surroundings. Generally, it is not possible in a brain tumour to completely remove it considering other tumours in the body.

Surgery
Surgery is the first and foremost way to treat Glioblastoma Multiforme. On an average, the tumour has 1,00,000,000,000 cells. On surgery, it gets reduced by 98%. Even removing a portion of the tumour can reduce the signs and symptoms. Surgery to remove glioma carries risks like infection and bleeding. Tumour can not be removed from the surroundings as they are located near the sensitive areas of the brain.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be taken orally or intravenously as required by the patient. This treatment is now standard for most cases of glioblastoma. Side-effects of chemotherapy depend on the dose and type of drugs like nausea, vomiting, hair loss, loss of appetite, fever, weakness, low immunity, skin rashes, irritation.
Radiation
Regardless of the advanced diagnostic procedure and multi-treatment which includes maximal surgical resection, followed by radiotherapy along with maintenance temozolomide chemotherapy; almost all patients experience tumour progression. Radiation uses high energy beams such as X-rays or protons to kill tumour cells.
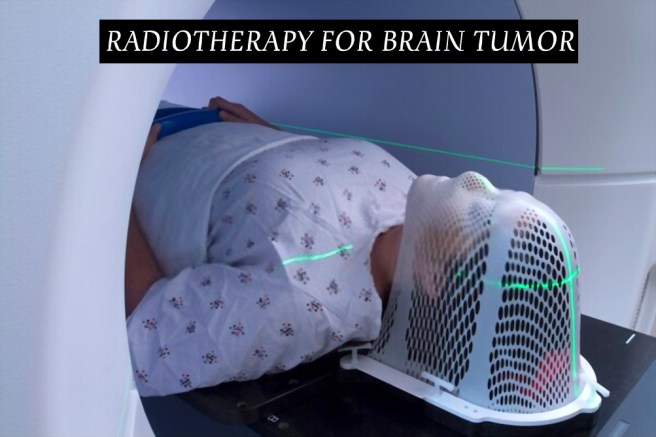
The type of glioma one has, its grade and other prognostic symptoms are considered in determining the timing and type of radiation therapy a patient may receive. There are different types of radiation therapy:
- Using a computer system to pinpoint delivery
Techniques include intensity-modulated radiation therapy and 3D conformal radiation therapy. With the help of computers radiation therapy to the exact location of the brain tumour.
- Using Protons
This technique is called conformal proton beam therapy. The treatment starts once the proton reaches the tumour.
- Using multiple beams of radiation
This technique is called stereotactic radiation therapy. Every single beam of radiation is not particularly powerful, but the point where all the beams meet at the brain tumour receives a large dosage of radiation to kill the cancer cells in a very small area.
Radiotherapy includes side effects varying with the dosage and type of radiotherapy. The common side effects include fatigue, headache and scalp irritation.


