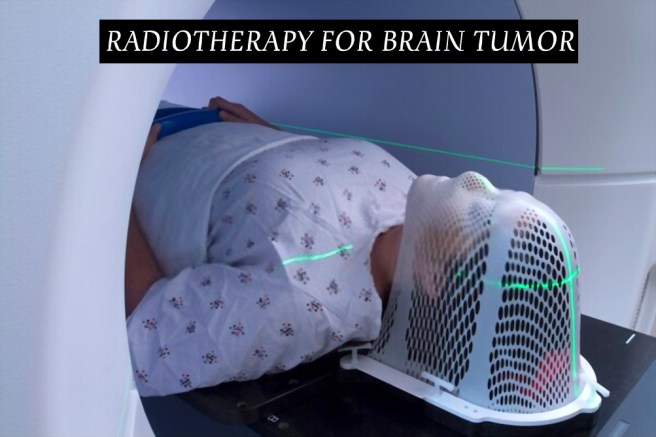
The patients get worried and overwhelmed at the beginning of cancer treatment. Acknowledging the treatment procedure and its benefits will help to ease the process. The information provided will boost the confidence on the treatment.
The oncologists often suggest cancer patients to go for Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for initial cancer treatment. The treatment involves the use of advanced computer programs to compute and deliver radiation directly to the cancer cells from different angles. It allows the cancer patient to receive higher and more effective doses of radiation. It also limits the damage to the healthy tissues and organs around the cancer cell. This added advantage of adopting the IMRT procedure increases the chances of cure and lessens the side effects.
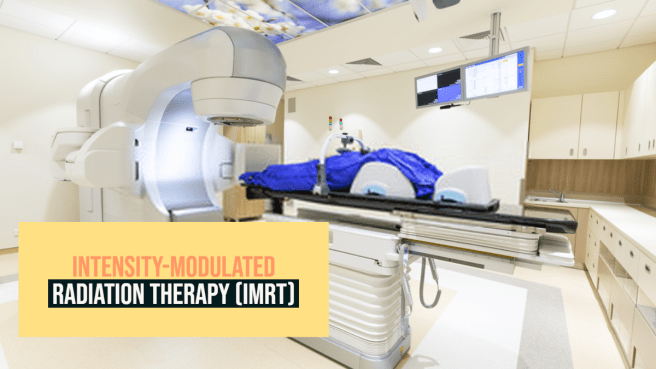
How does IMRT work?
Radiation therapy for cancer is often used to treat the tumor, which is located close to the critical organ and tissues. It is used to treat the following types of cancer:
- Prostate cancer
- Head and neck cancer
- Lung cancer
- Brain cancer
- Breast cancer
- Gastrointestinal cancer
- Lymphoma
- Sarcoma
- Gynecologic cancer
- Pediatric cancer
Treatment procedure
To treat the tumour cells, the patient will have to undergo an imaging test called a CT scan, which will help to map the tumour cell as a 3-D image. After mapping the image, the radiation experts use the advanced computer program IMRT. It helps to locate the tumour and delivers the radiation directly to the tumour cell from different angles.
The radiation therapist will position the patient on a treatment table and will make marks to help guide themselves and deliver the radiation treatment correctly. The IMRT treatment sessions are painless.
Benefits of IMRT
IMRT is mostly used when the tumour cells are present near critical organs. Once the session begins, it directs the radiation dose to focus on the three-dimensional shape of the tumour and modulates the radiation beams into multiple smaller beams. This helps to deliver a higher dose of radiation beams to reach the tumour cell while sparing the healthy tissues around it. Throughout the course of treatment, the machines form the radiation into varying shapes.
How long do IMRT sessions generally last?
The IMRT sessions generally take between 10 to 30 minutes. These sessions are quick and do not include pain. Patients have to undergo this treatment about 5 times per week. This schedule has to be followed for 3 to 9 weeks.
Even though the treatment has been reported to be painless by many, yet anaesthesia would be given to block the awareness of the pain. Most of the patients feel no discomfort, while some have experienced weakness and nausea from the anaesthesia. Radiation therapy affects the healthy tissues around it to some extent. So, it is recommended by the oncologist to take a 2-day pause in treatment every week to help the body repair the damages. The treatment requires the patient to stay for a couple of hours in the hospital.
After the radiotherapy in Bannerghatta road, the oncologists keep a check on the impact of the treatment on the patient. The report generation is done at least once a week. If needed, the treatment plan will be adjusted by the oncologists as per the requirements of the patient.
Often people experience fatigue, emotional distress, and sensitive skin at the site of the radiation beam exposure. The oncologists have suggested that the patients have to take care for themselves by following a proper diet chart, getting extra sleep will be beneficial for the body, using lotions for skincare, and minimizing the sun exposure. As the body will recover, the patient will have to go for fewer visits to the doctor.